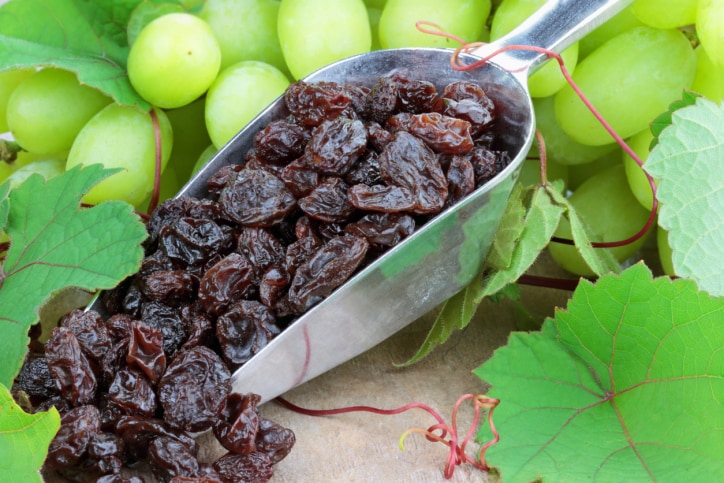
A member of the grape family, currant is a dry, dark-red and seedless raisin. Often considered along with gooseberry, currants are commonly used for making food preservatives, liqueurs and syrups. Currants are usually not eaten raw for their tarty taste.
Types
There are a wide variety of currants differing in texture, color and fruit flavor. Very commonly used varieties are blackcurrant, redcurrant and whitecurrant.
Blackcurrant can be eaten raw but it carries a very strong tarty flavor. The fruit has to be blended with sweetening agents to be toothsome. For regular culinary use, the fruit is steamed with sugar to produce a puree, which is used as an ingredient in cheesecakes, yogurt, ice creams, desserts and several sweet dishes.
Red currant variety range in varied shades – from dark red to pink, yellow or white. Their sweetness increases as the color of the fruit intensifies. It is often served raw or as a simple add-on with salads or drinks. In United Kingdom, redcurrant jelly is served along with lamb on Sunday toast.
Unlike the black and red currants, white currant is usually cultivated for their ornamental value. This variety of currants is relatively sweeter. When prepared into jams and jellies, it yields a pink color.
Nutritional value
1. White currants are good source of Vitamins B1 and C1. They also have rich amounts of iron, manganese and copper.
2. Blackcurrants are low-fat and high-protein berries.
3. Blackcurrants contain glucose that provides necessary energy required to the body.
Did you know?
For their tarty taste, black currants were once looked upon as inferior berries.
Between the period of 1600s and 1700s, American colonists began cultivating currants and imported to Europe.
[“source-ndtv”]