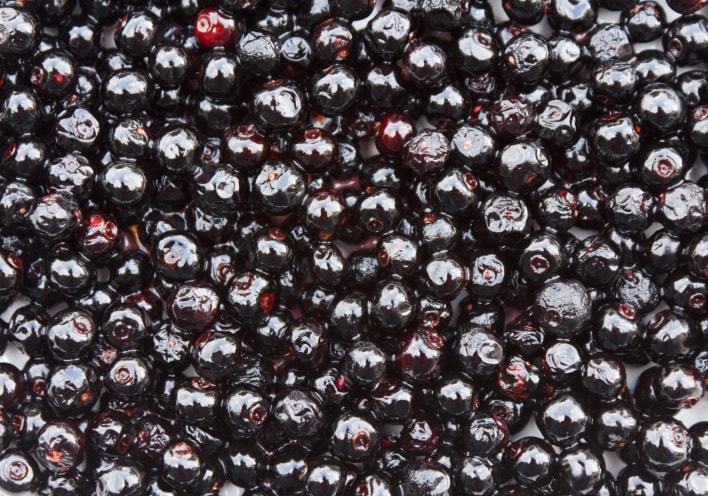
Known by various names like jambul, jambas etc, this purple berry has a unique taste, color and flavor. For its resemblance, jamun is always misinterpreted as blackberrry.
Predominantly sweet, it also plates a acidic flavor which warrants the use of salt while eating it. The most common variety is long and has a deep purplish color with a large seed, another common variety is seedless. The jambul tree is native to India. It is sweet tasting and acidic in nature due to which it is often eaten with salt. The leaves carry a mild oil similar to turpentine. They are mostly used as for for livestock owing to their nutritional value. For its acidic content, it is usually eaten with a pinch of salt sprinkled over.
Nutritional Value
Jamun is popularly used in Ayurvedic and Unani medicine. A special use is in the treatment of diabetes and digestive disorders like diarrhea. It’s dried seed powder also known to regulate blood sugar level. This purple tropical berry is laden with vitamin B, carotene, phytochemicals (antioxidants), magnesium, potassium and fiber. Jamun is known to be used as a treatment for diabetes. Ripe Jamun fruit also acts like a good liver stimulant.
Did you know?
The jamun can trace its ancestors to Philippines.
In many parts of the world like Israel and Algiers, the jamun tree has no value except ornamental.
[“source-ndtv”]